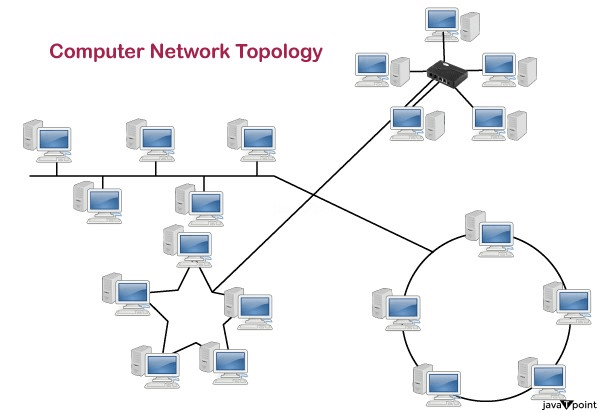
What is Topology?
Topology defines the structure of the network of how all the components are interconnected to each other. There are two types of topology: physical and logical topology.
Physical topology is the geometric representation of all the nodes in a network.
The bus topology is designed in such a way that all the stations are connected through a single cable known as a backbone cable.
Each node is either connected to the backbone cable by drop cable or directly connected to the backbone cable.
When a node wants to send a message over the network, it puts a message over the network. All the stations available in the network will receive the message whether it has been addressed or not.
The bus topology is mainly used in 802.3 (ethernet) and 802.4 standard networks.
The configuration of a bus topology is quite simpler as compared to other topologies.
The backbone cable is considered as a "single lane" through which the message is broadcast to all the stations.
The most common access method of the bus topologies is CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access).
CSMA: It is a media access control used to control the data flow so that data integrity is maintained, i.e., the packets do not get lost. There are two alternative ways of handling the problems that occur when two nodes send the messages simultaneously.
CSMA CD: CSMA CD (Collision detection) is an access method used to detect the collision. Once the collision is detected, the sender will stop transmitting the data. Therefore, it works on "recovery after the collision".
CSMA CA: CSMA CA (Collision Avoidance) is an access method used to avoid the collision by checking whether the transmission media is busy or not. If busy, then the sender waits until the media becomes idle. This technique effectively reduces the possibility of the collision. It does not work on "recovery after the collision".
Advantages of Bus topology:
Low-cost cable: In bus topology, nodes are directly connected to the cable without passing through a hub. Therefore, the initial cost of installation is low.
Moderate data speeds: Coaxial or twisted pair cables are mainly used in bus-based networks that support upto 10 Mbps.
Familiar technology: Bus topology is a familiar technology as the installation and troubleshooting techniques are well known, and hardware components are easily available.
Limited failure: A failure in one node will not have any effect on other nodes.
Disadvantages of Bus topology:
Extensive cabling: A bus topology is quite simpler, but still it requires a lot of cabling.
Difficult troubleshooting: It requires specialized test equipment to determine the cable faults. If any fault occurs in the cable, then it would disrupt the communication for all the nodes.
Signal interference: If two nodes send the messages simultaneously, then the signals of both the nodes collide with each other.
Reconfiguration difficult: Adding new devices to the network would slow down the network.
Attenuation: Attenuation is a loss of signal leads to communication issues. Repeaters are used to regenerate the signal.
========================================
Ring Topology
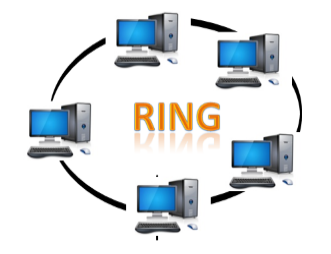
- Ring topology is like a bus topology, but with connected ends.
- The node that receives the message from the previous computer will retransmit to the next node.
- The data flows in one direction, i.e., it is unidirectional.
- The data flows in a single loop continuously known as an endless loop.
- It has no terminated ends, i.e., each node is connected to other node and having no termination point.
- The data in a ring topology flow in a clockwise direction.
- The most common access method of the ring topology is token passing.
- Token passing: It is a network access method in which token is passed from one node to another node.
- Token: It is a frame that circulates around the network.
Working of Token passing
- A token moves around the network, and it is passed from computer to computer until it reaches the destination.
- The sender modifies the token by putting the address along with the data.
- The data is passed from one device to another device until the destination address matches. Once the token received by the destination device, then it sends the acknowledgment to the sender.
- In a ring topology, a token is used as a carrier.
Advantages of Ring topology:
- Network Management: Faulty devices can be removed from the network without bringing the network down.
- Product availability: Many hardware and software tools for network operation and monitoring are available.
- Cost: Twisted pair cabling is inexpensive and easily available. Therefore, the installation cost is very low.
- Reliable: It is a more reliable network because the communication system is not dependent on the single host computer.
Disadvantages of Ring topology:
- Difficult troubleshooting: It requires specialized test equipment to determine the cable faults. If any fault occurs in the cable, then it would disrupt the communication for all the nodes.
- Failure: The breakdown in one station leads to the failure of the overall network.
- Reconfiguration difficult: Adding new devices to the network would slow down the network.
- Delay: Communication delay is directly proportional to the number of nodes. Adding new devices increases the communication delay.
==================================
Star Topology
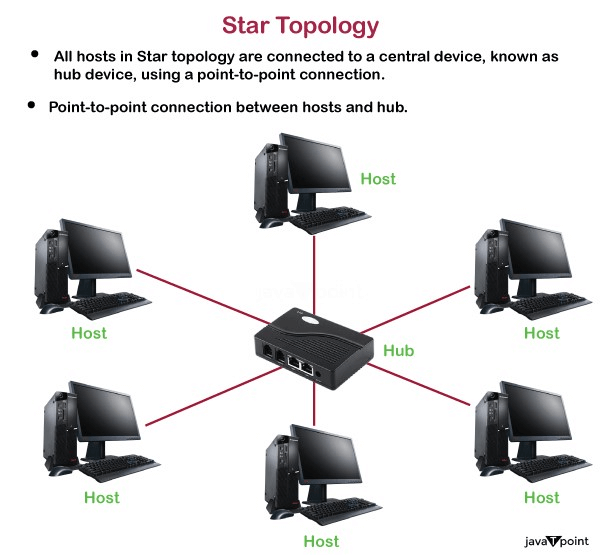
- Star topology is an arrangement of the network in which every node is connected to the central hub, switch or a central computer.
- The central computer is known as a server, and the peripheral devices attached to the server are known as clients.
- Coaxial cable or RJ-45 cables are used to connect the computers.
- Hubs or Switches are mainly used as connection devices in a physical star topology.
- Star topology is the most popular topology in network implementation.
Advantages of Star topology
- Efficient troubleshooting: Troubleshooting is quite efficient in a star topology as compared to bus topology. In a bus topology, the manager has to inspect the kilometers of cable. In a star topology, all the stations are connected to the centralized network. Therefore, the network administrator has to go to the single station to troubleshoot the problem.
- Network control: Complex network control features can be easily implemented in the star topology. Any changes made in the star topology are automatically accommodated.
- Limited failure: As each station is connected to the central hub with its own cable, therefore failure in one cable will not affect the entire network.
- Familiar technology: Star topology is a familiar technology as its tools are cost-effective.
- Easily expandable: It is easily expandable as new stations can be added to the open ports on the hub.
- Cost effective: Star topology networks are cost-effective as it uses inexpensive coaxial cable.
- High data speeds: It supports a bandwidth of approx 100Mbps. Ethernet 100BaseT is one of the most popular Star topology networks.
Disadvantages of Star topology
- A Central point of failure: If the central hub or switch goes down, then all the connected nodes will not be able to communicate with each other.
- Cable: Sometimes cable routing becomes difficult when a significant amount of routing is required.
=========================================
Hybrid Topology
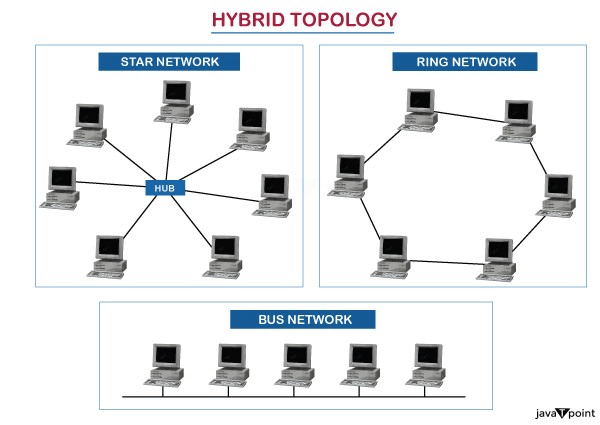
- The combination of various different topologies is known as Hybrid topology.
- A Hybrid topology is a connection between different links and nodes to transfer the data.
- When two or more different topologies are combined together is termed as Hybrid topology and if similar topologies are connected with each other will not result in Hybrid topology. For example, if there exist a ring topology in one branch of ICICI bank and bus topology in another branch of ICICI bank, connecting these two topologies will result in Hybrid topology.
Advantages of Hybrid Topology
- Reliable: If a fault occurs in any part of the network will not affect the functioning of the rest of the network.
- Scalable: Size of the network can be easily expanded by adding new devices without affecting the functionality of the existing network.
- Flexible: This topology is very flexible as it can be designed according to the requirements of the organization.
- Effective: Hybrid topology is very effective as it can be designed in such a way that the strength of the network is maximized and weakness of the network is minimized.
Disadvantages of Hybrid topology
- Complex design: The major drawback of the Hybrid topology is the design of the Hybrid network. It is very difficult to design the architecture of the Hybrid network.
- Costly Hub: The Hubs used in the Hybrid topology are very expensive as these hubs are different from usual Hubs used in other topologies.
- Costly infrastructure: The infrastructure cost is very high as a hybrid network requires a lot of cabling, network devices, etc.





Comments
Post a Comment